Research papers are known for two things: long hours scouring for relevant citations, and extensive submission windows. But not anymore.
With a single additional feature called deep research, ChatGPT aimed to create an availability that cancelled typical long research hours and reduced them to structured prompts and minutes of detailed research reports.
I tried ChatGPT’s deep research on a likely seminar research topic to determine how reliable this claim has been since the feature’s rollout. Below, you’ll read all about it and much more critical stuff uncovered during the process.
Keep reading.
TL;DR: 8 key takeaways from ChatGPT Deep Research Review
- ChatGPT’s Deep Research is OpenAI’s most advanced research agent. Launched in early 2025, it runs on the O3 model for Pro/Enterprise users and a simplified O4-mini version for free/Plus plans.
- It’s completely free within your existing ChatGPT plan—free users get 5 tasks/month, Plus/Enterprise users get 25 tasks/month, and Pro users get 250 tasks/month.
- The tool automatically breaks down complex questions into multiple research components instead of trying to answer everything at once.
- It pulls real-time information from hundreds of web sources with inline citations and explains why each source was chosen for credibility.
- There’s a hidden 1,300-character prompt limit that can cause the tool to fail silently—you need to keep requests concise and focused.
- Processing speed is incredibly fast. My test on Nigerian education barriers took just 7 minutes to analyze 46 sources through 135 searches.
- The citations are accurate, but some promised features are missing, like data tables/graphics that might not appear despite being requested and confirmed.
- Success requires specific, research-quality prompts, such as timeframes, geographic scope, and source types, rather than vague questions.
What is ChatGPT Deep Research?
Deep Research is OpenAI’s most advanced research agent, built to operate independently and with the associated characteristics of a skilled analyst. Introduced in early 2025, it runs on OpenAI’s o3 model for Pro and Enterprise users. A simplified version, powered by o4-mini, is available for users on free and Plus plans.
To use it, you provide a prompt, and it systematically searches, interprets, and synthesizes data from hundreds of online sources to produce a comprehensive, evidence-backed report..
Built on a specialized version of OpenAI’s o3 model, Deep Research is optimized for both web browsing and large-scale data analysis. But it does more than just gather information. It actively reasons through conflicting sources, adjusts its approach as new insights emerge, and shifts focus when necessary to deepen its understanding.
This agent can analyze text, images, and PDFs across the web, identifying patterns, contradictions, and context across vast volumes of content, all without user micromanagement. The output is not a surface-level summary, but a deeply structured synthesis: transparent, traceable, and often at the level of professional policy, business, or academic research. Below, the features are explained.
ChatGPT Deep Research key features
Multi-step query decomposition
ChatGPT Deep Research doesn’t try to answer complex questions in a single pass. Instead, it automatically breaks them down into multiple logical subcomponents. For example, a request about electric vehicle regulations in Europe might be separated into policy trends, country-specific laws, and economic impacts, each researched independently. This modular approach creates more structured, organized, and comprehensive answers.
Real-time web retrieval with source reasoning
Unlike regular GPT responses, Deep Research pulls current information directly from the web. It actively evaluates the credibility of sources, provides citations inline, and explains why a particular reference was chosen. This keeps the information current and allows readers to follow the reasoning process behind each conclusion.
Source transparency and evidence awareness
Every statement made through Deep Research is tied to a specific source, with the citation placed where it’s most relevant. This transparency lets users verify information for themselves and helps reduce the risk of AI hallucinations by foregrounding evidence over speculation. It is particularly valuable in fields where reliable, verifiable claims are essential.
Multi-Part Findings
Once the data has been gathered, Deep Research synthesizes it into a cohesive long-form output. It integrates information from across sources, highlighting points of agreement, disagreement, or uncertainty where they occur. This synthesis goes beyond basic summarization by connecting facts in a reasoned, logical sequence, resulting in thorough, contextually rich answers.
Who can access ChatGPT Deep Research and at what cost?
ChatGPT’s Deep Research feature is now widely accessible across various user tiers, offering surprisingly generous limits, even to free users. Unlike some premium-only features, OpenAI has designed Deep Research to be available at no extra charge within the monthly subscription plans, with a clear, task-based quota system.
Let’s break down who can access it and what usage limits apply:
Free Plan Users
- Free-tier users can run 5 Deep Research tasks monthly using a lightweight feature version.
This version is still competent but slightly less robust than the standard model used in paid plans.
Plus, Team, Enterprise, and Edu Plans
- These users get 10 Deep Research tasks per month with the standard model.
- In addition, they receive 15 extra tasks per month using the lightweight version once the standard limit is reached.
- After the standard model quota is used, Deep Research automatically switches to the lightweight version without disrupting your workflow.
Pro Plan Users
- Pro users enjoy the highest allowance: 125 monthly tasks using the standard model.
- Once that’s exhausted, they can continue with another 125 tasks using the lightweight model, bringing the total to 250 tasks/month.
To take in everything better, here’s a quick breakdown:
| Plan | Standard Model Tasks | Lightweight Model Tasks | Total Tasks/Month |
| Free | 0 | 5 | 5 |
| Plus/Team/Enterprise/Edu | 10 | 15 | 25 |
| Pro | 125 | 125 | 250 |
How To Use ChatGPT Deep Research (Step-by-step guide)
Using ChatGPT Deep Research is simple once you understand where to look and how to prompt it correctly. Here’s a complete walkthrough to help you get started.
Step 1: Make sure you’re eligible
First, confirm that you’re on a supported plan (Plus, Pro, Team, or Enterprise). The free tier does not allow you to access Deep Research’s full capabilities.
Step 2: Launch ChatGPT and select GPT-4
Go to chat.openai.com. In the top-left model selector, choose GPT-4. Deep Research is not available under GPT-3.5.
Step 3: Look for the Research Tool
You should see a “Research” tool enabled in your session.
If not, click the “Settings”, under that find and open “Tools” and make sure Research is toggled on.
Step 4: Write a good prompt
Start your prompt with a direct request. Examples:
- “Compare EV adoption in Japan vs South Korea.”
- “I want a detailed report on the impact of inflation on economies.”
There’s a detailed tip here.
Step 5: Let it run
After you submit your prompt, ChatGPT will ask clarification questions. After you answer, it will confirm your response and initiate a search.
You’ll see a progress bar loading like this. Behind this progress bar, ChatGTP Deep Research is carrying out tasks like:

- Breaking down the query
- Investigating sub-questions
- Gathering citations
- Compiling the response
- It may take 5–30 minutes, depending on complexity.
Step 6: Read the final output carefully and verify information
You’ll receive a structured report that includes:
- Subheadings
- Inline citations
- Bullet points or summaries
- A list of sources at the end
You can click the citations to view the original pages. The tool usually links directly to articles, whitepapers, government documents, or reputable outlets.
Step 7: Ask follow-up questions
You can extend or refine the investigation by asking based on your niche. For example,
- “Add a section on …..”
- “Compare your findings to ….”
- “Use academic papers instead of news sources.”
If it builds on the existing thread, each follow-up counts as part of the same research run.
PS: The essence of the make-up prompts in this review is to give you a sense of how to set up your search. Please do not use them unless they align with your research goal.
Step 8: Check Your quota
If the tool stops responding or alerts you that you’ve reached your quota, click on your account and go to “My Plan” to view how many full and lightweight research runs are left.
By following these steps, you’ll get the most out of what Deep Research offers and avoid wasting your monthly runs.
I put ChatGPT’s Deep Research to the test – here’s what happened in 7 minutes
I began this Deep Research testing with a topic I knew would challenge the system. I wanted it to be something sequential, political, and deeply tied to real-world complexity. After a while of pondering, that turned out to be why educational equity across Nigeria’s six geopolitical zones remains so difficult to achieve, and what systemic barriers keep progress fragmented or stalled
To start, I drafted a thorough and well-structured prompt. It was detailed and precise, including multiple angles such as ethnic tensions, climate vulnerability in the North, failures of the Universal Basic Education Act, uneven program implementation, unintended consequences of cash transfers, and the complex political ecosystem surrounding education policy in Nigeria. I even requested projections for 2050.
Feeling confident, I pasted the full prompt into the Deep Research investigation box and hit enter.
And nothing happened. There weren’t any follow-up questions, just a blank response and a quiet error. I tried again, this time reformatting slightly by spacing differently and adjusting the words, but it still failed to process. That’s when I realized something important: ChatGPT’s Deep Research has a hidden but very real character limit.
After a quick check on Google Docs, I found that my original prompt was about 1,685 characters long (with spaces).
So I tried ChatGPT’s deep research feature on another device.
While Deep Research handled my longer prompt in that session, I learned through trial and error that its processing limit isn’t consistent. In some instances, a prompt of over 1,600 characters worked flawlessly. In others, the same prompt failed to load with no error. This suggests a flexible but unpredictable cutoff rather than a strict character limit, likely affected by system load and model behavior. For reliability, trimming prompts to under 1,300 characters or breaking them into smaller parts yields more consistent results.
This is a crucial limitation, and it’s not always obvious. When designing prompts to test a model’s capabilities (especially for something called “Deep Research”), you naturally assume you can go as deep as you like. But this discovery taught me that you have to be strategic in what you ask and how you ask it.
So I went back to my draft and began trimming it down. Instead of asking everything in a single go, I restructured the request into one tightly focused version that stayed within 1,300 characters, like this:
Instead of immediately getting into research, ChatGPT asked me questions. Four specific ones:
What kind of report did I want—executive summary or full research paper? I wrote a five-page report. Who was my audience—academics, NGOs, government? I chose an academic paper. Did I want data tables and graphics? Yes. What tone—formal academic or something else? I chose an academic tone.
It followed the basic seminar research steps taught in lecture halls. So, it made further inquiries that it at least got the memo. Then it confirmed everything back to me: “I’ll conduct a comprehensive academic investigation into the systemic barriers preventing educational equity across Nigeria’s six geopolitical zones. The final output will be a five-page report in academic tone, including data tables and graphics where available….”

I hit the enter key at 7:31 AM and watched it start working.
What happened next was remarkable. I could see it thinking, processing, and connecting dots across multiple areas—ethnic and religious tensions, economic disparities, climate change in the North, security issues, gender bias, language policies, and infrastructure gaps. It wasn’t just collecting random facts. It was building a complete picture.
Seven minutes later, at 7:38 AM, my screen filled with results that made me stop and stare.
The numbers were staggering: 46 sources, 135 searches, all compiled while I was barely finishing my morning coffee. But the real shock was the depth and connections it made.
It revealed that over 10 million Nigerian children are out of school, with nearly two-thirds being girls. In the northeast, female attendance drops to just 48% because of conflict. The research showed how Boko Haram’s “Western education is forbidden” slogan led to 276 Chibok girls being kidnapped and over 512 schools being destroyed in Borno by 2014.
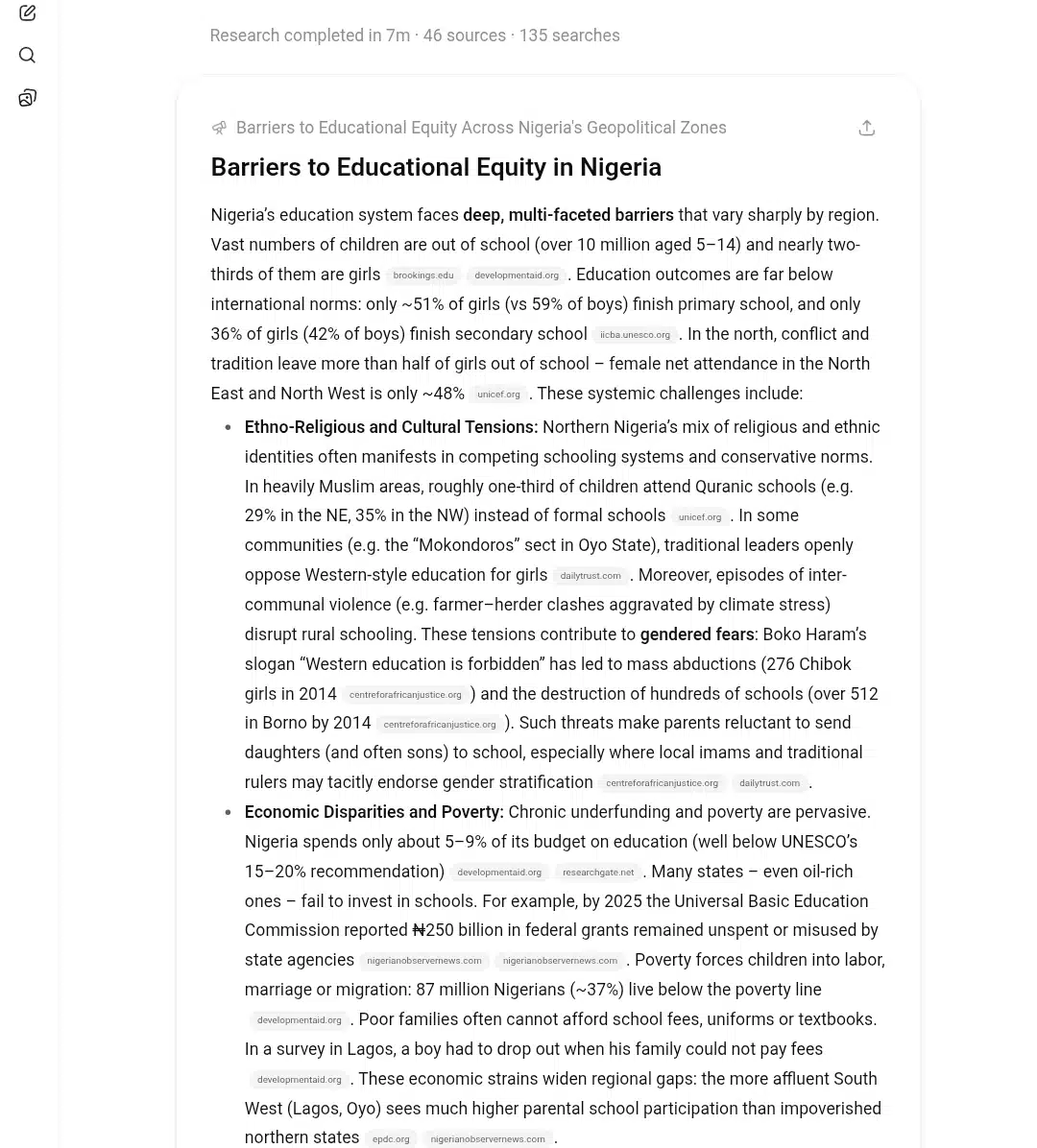
But here’s what impressed me most—it didn’t just list problems in isolation. It showed how everything connects. Climate stress leads to farmer-herder conflicts, which destroy schools. Parents become afraid to send their children, especially girls. Traditional leaders sometimes resist Western education. Oil companies try to help, but create new tensions with communities.
The regional breakdown was eye-opening. In the southwest, Oyo State reduced out-of-school rates to 12% through aggressive campaigns. Meanwhile, conflict has made education nearly impossible in the northeast – fewer than 1 in 3 girls complete primary school in some areas.

It even looked ahead to 2050, warning that Nigeria’s population could hit 400 million. With 43% currently under 15, a massive youth percentage will need education and jobs.
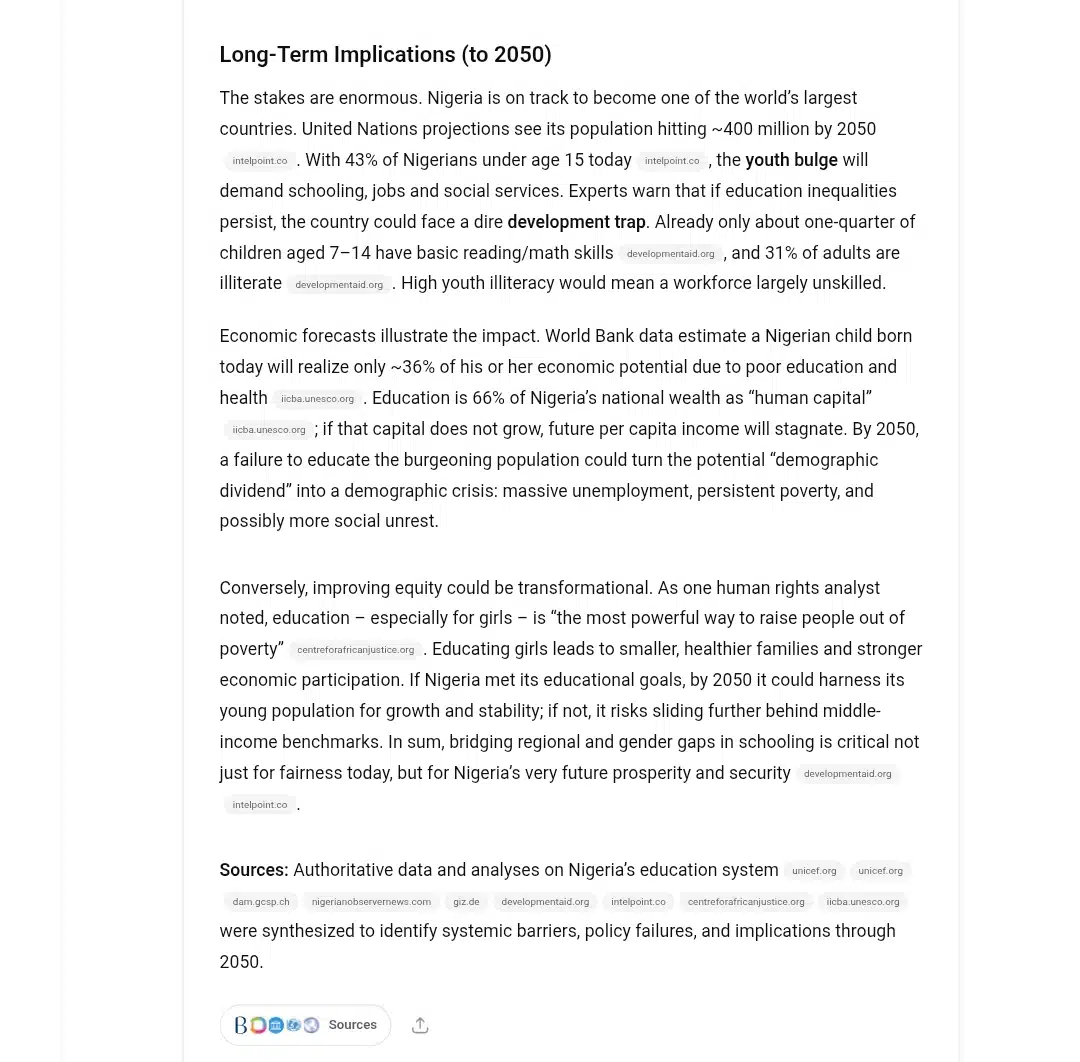
ChatGPT’s Deep research took seven minutes to produce a seminar research that would have taken me weeks to compile myself. Connected dots I might never have seen, using sources I wouldn’t have known to look for. This wasn’t just about speed but about access to comprehensive analysis on complex topics.
But it wasn’t all done and packed with this. I had to verify the citations and see what aligned or not because AI makes mistakes. However, the hours of refinement and verification would be relatively shorter than the whole process of researching, writing, and sourcing.
Now, to balance my testing experience, I’ll discuss the pros and cons of ChatGPT’s deep research.
Pros and Cons of using ChatGPT Deep Research
Pros
Research-level output in minutes
The single most striking advantage of Deep Research is its speed. What would’ve taken me days or even weeks to compile manually came together in seven minutes. And this wasn’t just a surface-level scan of Wikipedia articles. It built layered connections, ethnic tensions linking to security issues, climate instability linking to education dropouts, all contextualized across Nigeria’s geopolitical zones. That kind of synthesis, at that pace, was something I hadn’t seen before in any research tool, AI-powered or not.
Context-aware citation matching
The citations weren’t just fake. I tested several of the hyperlinks embedded in the report—each one opened cleanly and led to actual sources that directly supported the specific claim next to it. No phantom links, no misleading attribution. And while I’m aware AI tools can sometimes misattribute sources, in this case, the quality and alignment of the references were surprisingly strong. That made it easier to trust (but also to verify) what I was reading.
Guided prompt refinement
Once I reduced my original prompt to the model’s workable limit (around 1,300 characters), it didn’t just launch into a generic response. It asked clarifying follow-ups: “Who is your audience?” “What kind of report are you expecting?” “Should the tone be academic?” These weren’t filler questions; they were strategic filters that helped narrow the research lane and made the final result feel customized, not pre-set.
Structural discipline in the writing
What I received wasn’t a loosely formatted info dump. The output had clear headings, subheadings, structured sections, and data tables where needed. It followed an academic format almost instinctively. That matters when you’re doing real-world work because copying and pasting into a Word doc or presentation becomes much faster when the format is already intact.
It connects the macro and micro information
I appreciated how the final research didn’t isolate numbers from narratives. It cited national-level figures (like the over 10 million out-of-school children). It zoomed into state-specific cases like Oyo State’s progress or the collapse of girl-child education in Borno. This kind of vertical layering, from federal to state to individual impact, helped me visualize the ecosystem of barriers, not just the statistics.
Cons
Did not include tables or graphics despite confirming
Even though I selected the data tables and visuals option during the setup phase and the model acknowledged this request, the final research output didn’t include a single chart, table, or graphic. The absence of structured data presentation was a noticeable gap for a tool aimed at academic-level output.
No inline fact warnings
Although the citations were strong in this case, no feature alerts you when a specific stat or claim might be outdated or questionable. You still need to do manual fact-checking if accuracy matters to you. Unlike some tools that mark facts as “unverified” or “needs checking,” Deep Research doesn’t flag any uncertainty; it presents everything as final. That puts more responsibility on the user to cross-verify.
No way to revise without a new prompt
Once the prompt is entered and processed, you can’t edit or adjust it without starting the whole process. If you think of a better way to phrase your question or want to adjust the audience type or tone, you have to resubmit everything from scratch. A light revision feature would’ve been helpful, especially for iterative research.
Occasional overreach in projections
While my report’s 2050 projection was well-supported, I noticed instances where it relied heavily on extrapolated trends without always making the underlying assumptions explicit. If you’re not careful, this could be problematic in areas like demography or policy. You’ll want to examine those sections critically rather than accept them as definitive forecasts.
So, Deep Research delivers exceptional value when it works within its lane. It’s fast, precise, deeply referenced, and structurally organized. It’s the kind of tool that can truly accelerate policy writing, academic reports, NGO briefs, and other similar tasks. But it’s not entirely intuitive yet. You need to be aware of its prompt limitations, be prepared to verify citations, and understand that it’s still a one-shot process with no back-editing.
For me, though, the benefits clearly outweighed the limitations. I now understand how to work within its constraints, making it one of the most resourceful research tools I’ve used this year.
Tips for getting the best results from ChatGPT’s Deep Research
Because Deep Research has a limited number of runs, every query should be treated with care. If you want rich content and trustworthy responses, you need to design your prompts like a researcher would. Below are the best practices to help you get consistently high-quality results.
1. Ask a researchable, specific question
The single most significant predictor of a successful result is the quality of your question. A vague request like “Tell me everything about AI” will either be rejected or return something too broad to be useful. A strong Deep Research prompt has a clear focus, scope, and objective. You can drastically improve your chances by writing your prompts about how a researcher frames a topic.
Some strong examples that come to mind include:
- “Compare AI safety regulations in the EU vs the US from 2021 to 2024.”
- “Summarize current strategies for tackling water scarcity in rural Kenya.”
- “Trace the rise of lithium demand in battery production post-2020.”
- Inversely, weak examples would sound like this:
- “Talk about climate change in ….”
- “What’s going on in politics in….?”
- “Write a research on space in .”
Deep Research thrives most when you ask it to trace something clearly definable.
2. Add timeframes to focus the scope
Another simple way to increase the relevance of your output is to pin down the time range you’re interested in. This helps the system limit what it fetches and prioritize sources that match the period.
You can phrase your timeframe in natural language:
- “Between 2020 and 2024”
- “In the past 12 months”
- “Since COVID-19”
- “During the (name) administration”
This small detail pushes the model beyond general background knowledge and focuses on recent or timely information.
3. Request source types (and be specific)
You can also guide Deep Research toward more appropriate content by telling it what kinds of sources to use or avoid. If you’re doing academic work, this is especially important.
You can say things like:
- “Use peer-reviewed medical studies only.”
- “Avoid blog posts or Reddit threads.”
- “Prioritize data from government and NGO reports.”
- “Include at least one financial analysis.”
The system will mix articles, reports, and sometimes opinion pieces if you don’t say anything. This instruction helps the tool better match your needs.
4. Use comparative or analytical verbs in your prompts
The prompt verbs you use shape the structure and purpose of the report. Verbs like compare, analyze, evaluate, summarize, trace, and identify all suggest a focused, answerable task.
These verbs are action-oriented, and AI responds to them very seriously.
5. Follow Up Like a Human Researcher Would
Deep Research isn’t just a one-shot tool. Once you get a report, you can ask for follow-up briefs based on gaps, new angles, or critiques.
For example:
- “Add a section covering ‘this’ to sections ‘these”.
- “Now include the perspective from developing countries.”
- “List recent counterarguments to this position.”
- “What changed after 2022?”
This lets you build on the report iteratively, just as a real researcher would go deeper after each supervisor’s correction.
6. Check sources for accuracy and existence
Each Deep Research report includes citations with links, but that doesn’t mean you should trust them unquestioningly.
Here’s how to verify:
- Click through to the original links.
- Check if the page still exists.
- Confirm that it says what the report claims.
- Look at the publication date and the author’s credibility.
Deep Research is surprisingly good at citing real, high-quality sources, but it’s not immune to occasional overgeneralization. Manual confirmation is a must for any critical use (especially in journalism, academic work, or public writing), and you can get it down with the suggestions on the bullet points above.
7. Don’t waste runs on joke or open-ended prompts
Deep Research is limited to a set number of daily runs per user (as of now, 5). That’s enough for serious work, but it’s not plentiful. So you should avoid running prompts like:
“Write a poem about the history of tech.”
“What’s the meaning of life?”
“Give me a list of memes about politics.”
It counts every time you use it (even if you abort). This isn’t just about conservation. So please don’t use it when you’re going down a curious hole or bored and don’t want to get off your phone. Use ChatGPT’s regular search box if you’re in such a mood. That has no usage limits, so it keeps going as long as your questions keep coming.
With these 7 prompt designs, you increase your chances of getting a more solid answer that meets your expectations. However, bear in mind AI’s limitations: it cannot verify information, so do yourself a favor and refine accordingly.
What makes ChatGPT Deep Research different from regular GPT-4 or web browsing
The key difference between Deep Research and regular GPT-4 browsing is purpose. While GPT-4 with browsing can fetch links and summarize webpages, Deep Research builds a multi-step research report with structured reasoning, like an analyst working from scratch.
The technical build-up and delivery also differ. While GPT-4 browsing reads pages in real time, ChatGPT’s Deep Research generates an internal research plan first, then queries and evaluates each component, before synthesizing everything into a clean narrative. This makes Deep Research more accurate for complex questions, but also slower and more demanding. For instance, you might get:
- 20+ cited sources
- Tables and comparisons
- Named risks and benefits
- Different writing forms from literature, law, medicine, and current affairs
The citations are clickable, and in many cases, Deep Research gives you a heads-up on when a source may not be reliable. It also explains its reasoning process in plain language, helping you understand how it formed its conclusions.
Here’s what I’m trying to say:
| Feature | GPT-4 with Browsing | Deep Research |
| Speed | Near-instant (under a minute) | Slower (5–30 minutes typical) |
| Research Style | Surface-level retrieval | Multi-step, structured reasoning |
| Output Format | Ad-hoc paragraphs or bullet points | Formal reports with headings and citations |
| Use of Sources | Summarizes webpages | Extracts, compares, and evaluates multiple |
| Citations | Rare or informal | Always provided, both inline and listed |
| Content Depth | Moderate, often < 500 words | High, ranging from 1,000 to 5,000 words |
| Follow-Up Handling | Basic, single-threaded | Thread-aware, expands and refines across turns |
So, use GPT-4 for
- Quick fact checks or news updates
- Summarizing a single page
- Verifying whether a topic is covered on a specific site
Choose ChatGPT Deep Research for
- Writing long-form essays, whitepapers, or reports
- Comparing positions across different countries or academic fields
- Tracing trends or concepts over time through multiple sources
- Sourcing hard-to-find data from scattered or inconsistent pages
If Deep Research and regular GPT-4 browsing were actually different people being asked a question by you and me, the former would answer as a seasoned research analyst, and the latter a virtual assistant with 4 clients.
ChatGPT Deep Research Alternatives
1. Microsoft Bing Chat (Copilot) – best for enterprise
Microsoft Bing Chat, now integrated into Microsoft Copilot, launched in early 2023, powered by GPT-4. It combines conversational AI with real-time web search, making it ideal for current research needs.
Why it’s a strong research alternative: Unlike ChatGPT’s knowledge limitations, Bing Chat provides real-time information with direct source citations. Its integration with the Microsoft ecosystem enables seamless workflow from research to documentation.
Microsoft Bing AI (Copilot) Features
- Real-time web search with source citations
- Multiple conversation modes (Creative, Balanced, Precise)
- Microsoft Office integration
- Image analysis capabilities
- Enterprise-grade security
Pricing
- Free: Basic access with daily limits
- Enterprise: $5/user/month or included in Microsoft 365
- Copilot: $30/user/month for advanced features
Pros
- Free tier is available with basic functionality for personal users
- Excellent integration with the Microsoft Office suite and Windows space
- Provides real-time information access with direct source citations
- Enterprise-grade security features ensure data protection for business use
Cons
- Daily query limits on the free tier restrict heavy research usage
- Requires a Microsoft account to access full functionality and features
- Can produce inconsistent results when handling creative or complex tasks
2. Perplexity AI – best for academic research
Founded in 2022, Perplexity AI focuses exclusively on research and information discovery. Explicitly built for accuracy and source verification, it has become the go-to choice for academic and professional researchers.
Why it’s a strong research alternative: Perplexity excels with comprehensive source citations and fact-checking. Its Copilot feature asks clarifying questions to refine research, while Collections organize research topics systematically.
Perplexity AI Features
- Comprehensive source citations with direct links
- Multiple AI models (GPT-4, Claude 3, Grok-2)
- Copilot guided research with clarifying questions
- Collections for organizing research projects
- File upload support (PDFs, CSVs, images)
- Focus modes for specialized research
Pricing
- Free: Limited daily queries
- Pro: $20/month with unlimited queries and premium models
- Enterprise: $40/user/month
- API: Starting at $3 for credits
Pros
- Excellent source citation system makes it ideal for academic and professional research
- Access to multiple premium AI models, including GPT-4, Claude 3, and Grok-2
- Research-focused design with specialized features like Collections and Focus modes
- Strong free tier provides substantial functionality for basic research needs
Cons
- Limited creative content generation compared to other AI platforms
- Subscription is required for heavy research usage and premium features
- No direct integration with popular productivity suites like Microsoft Office
3. Google Deep Research (Gemini Advanced) – best for structured analysis Google Deep Research
Google Deep Research is part of Gemini Advanced, representing Google’s premium AI research assistant. It automates multi-step research processes and creates comprehensive reports using Google’s vast search capabilities.
Why it’s a strong research alternative: Deep Research conducts thorough, structured research that mimics human methodology. It develops research plans, explores multiple angles, and synthesizes findings into comprehensive reports with file upload guidance.
Google Deep Research Features
- Multi-step automated research processes
- Research plan generation and methodology
- File upload integration for guided research
- Interactive report generation
- Google Search integration
- Gemini 2.5 Pro access with advanced reasoning
- Google Workspace collaboration
Pricing
- AI Pro: $20/month includes Deep Research
- AI Ultra: $250/month with high limits
- Student discount: Free Pro for one year
Pros
- Structured research methodology that mimics professional Research approaches
- Deep integration with Google’s cloud, including Search and Workspace
- Interactive report generation transforms research into engaging, shareable content
- Student discounts make it accessible for academic users with free Pro access
Cons
- Requires a paid subscription to access Deep Research functionality
- Limited to Google’s data sources and search ecosystem
- The platform is still developing with occasional inconsistencies in results
- Learning curve required to master advanced research features
4. Grok AI (xAI) – Best for Social Intelligence

Developed by Elon Musk’s xAI, Grok AI launched on November 4, 2023, with unique X (Twitter) integration. It offers real-time social media insights, built on custom architecture with massive computational power.
Why it’s a strong research alternative: Grok provides unique real-time social sentiment analysis and trend monitoring through X integration. It excels at complex analysis that is unavailable through traditional search engines.
Grok AI Features
- Real-time X (Twitter) integration for social trends
- Advanced mathematical and coding capabilities
- Massive computational power (100,000 H100 GPUs)
- Multi-modal processing (text, images, data)
- Social intelligence gathering
- Unfiltered, direct responses
Pricing
- Basic (Free Plan)
- Limited access to the Grok 3 model only
- No access to Grok 4’s advanced DeepSearch capabilities
- Basic search functionality with reduced performance
- SuperGrok ($300/year or $30/month):
- Full access to Grok 4 with integrated DeepSearch
- Replaces Grok 3 Think functionality with enhanced reasoning
- 128,000 token context memory for comprehensive research
- Voice with vision capabilities
- Unlimited usage within fair use policies
- SuperGrok Heavy ($3,000/year or $300/month):
- Access to Grok 4 Heavy before everyone else
- Double the context memory (256,000 tokens), which is perfect for handling massive research projects
- First to try new features when they launch
- Faster processing speeds and better performance, total package
Pros
- Unique access to real-time social media data provides insights unavailable elsewhere.
- Massive computational power enables complex analysis and mathematical calculation.s
- Advanced coding capabilities make it excellent for technical research projects
- Real-time trend monitoring helps track current events and social sentiment.
Cons
- Limited traditional web search integration compared to competitors
- Newer platform with fewer proven use cases and a smaller user community
- May provide controversial or unfiltered content that requires careful evaluation
Each platform serves different research needs depending on your requirements, budget, and research area.
Final verdict: Is ChatGPT’s Deep Research worth using?
Look, I’ll be straight with you. Deep Research impressed me way more than I expected. Getting research that would usually take me weeks done in 7 minutes? That’s impressive! The citations actually worked when I tested them. They led to real sources and connected each finding to another harmoniously.
But here’s the thing. That 1,300-character limit will trip you up if you don’t know about it. I wasted an attempt before figuring this out. And don’t expect those data tables they promised during setup. They might just not show up.
The speed and quality make it worth the cons, though. When it works, it really works.
Want to try it yourself? Go back to my step-by-step guide above and follow those exact steps. Then use the prompting tips I shared to avoid wasting your monthly limits. Trust me, you’ll want to be strategic about how you phrase things.
If this tool is as helpful for your work as it has been for mine, share this review with your colleagues. More people need to know about the potential and limitations of deep research.
ChatGPT Deep Research FAQs
1. How does Deep Research plan and structure its multi-step research process?
Deep Research uses a dynamic planning system that breaks down complex prompts into sub-tasks such as identifying key themes, verifying facts across multiple sources, and comparing differing viewpoints. It then executes these steps sequentially, often with conditional logic (something like, “If source A conflicts with B, highlight contradiction”). The end result is synthesized into a structured narrative or report.
2. What types of sources does Deep Research prioritize, and how does it choose them?
It prioritizes authoritative, high-signal domains, including .gov, .edu, major news outlets, research journals, and industry whitepapers. The algorithm evaluates page quality, topical relevance, citation density, and publication recency. Sources are dynamically selected during the research cycle and are ranked based on usefulness per topic segment.
3. Is Deep Research doing a real-time crawl or using a static index of sources?
Deep Research performs real-time web retrieval, not just searching a static index. It fetches and parses fresh content on demand, much like Bing AI or Google Search. It then summarizes, cross-references, and links citations based on relevance to the prompt.
4. How does Deep Research resolve conflicting information from multiple sources?
When encountering conflicting facts, Deep Research typically:
- Flags the disagreement
- Attributes each claim to its source
- Weighs credibility
- May offer contextual nuance (for instance, “The discrepancy likely results from differing definitions used in…”)
This method maintains neutrality while helping the reader make sense of ambiguity.
5. What limitations does Deep Research have regarding academic rigor or sourcing?
It’s not a replacement for academic literature reviews. It can’t access paywalled journals unless the content is available elsewhere. Also, citation styles are often informal and don’t meet APA/MLA/Chicago standards unless specifically requested. Still, it’s strong for preliminary research, content planning, and competitive analysis.
6. Can Deep Research produce biased or incomplete reports?
Yes, it can. Despite its structured process, Deep Research inherits biases from:
- The prompt itself
- The selection of online sources (for example, Western-centric publications)
- The weighting of popular vs. niche views
Careful prompt design, manual fact-checking, and follow-up queries can help mitigate these risks.
7. Can Deep Research cite academic papers from databases like JSTOR, PubMed, or Google Scholar?
No, not directly. It cannot bypass paywalls or access subscription-only databases. However, if publicly indexed, it may surface open-access versions of academic content or preprint repositories like arXiv or SSRN. Explicitly asking for academic sources can increase the likelihood of this.
8. Does Deep Research include multilingual or international sources?
Mostly not by default, it operates in English and primarily pulls from English-language sources. While it can theoretically summarize translated content, it does not automatically include global-language publications unless specifically prompted to do so (e.g., “Include non-English sources or regional coverage from Africa/Asia”).
9. Can Deep Research hallucinate citations, and how can I verify them?
It rarely hallucinates citations in the Deep Research mode because all sources are retrieved in real time. However, citations can be misattributed or overly summarized. To verify, check the clickable link, scan the page for the referenced claim, and confirm the date, author, and context.
10. How can I engineer better prompts for Deep Research to produce richer outputs?
Use specific, scoped prompts that include:
- A clear research goal (e.g., “policy comparison,” “cause-effect analysis”)
- Desired format (e.g., “comparative table,” “multi-part report”)
- Source preferences (“peer-reviewed,” “UN data only”)
- Regional scope if needed










