A probable scenario is you’ve been tasked to summarize a group of videos on a subject, and since you love a streamlined workflow, you decide to feed 5 video links to ChatGPT’s prompt bar to hasten things. But can ChatGPT watch those videos? The short answer is no—it cannot watch or stream videos directly, whether you use the free or paid versions. However, ChatGPT can still help you understand video content by summarizing transcripts, analyzing screenshots, and retrieving metadata like titles and descriptions.
In this article, you’ll discover how to use these workarounds effectively, understand the latest limitations, and learn everything else about ChatGPT and video content.
Let’s get on board!
What ChatGPT can do with video-related content
As already stated, ChatGPT cannot watch videos like humans do, but it has several capabilities that allow it to work effectively with video-related information. These functions rely primarily on text and static images derived from videos rather than direct video playback or audiovisual interpretation. Here is how ChatGPT watches a video without actually doing it in playback mode:

- Summarizes video content by analyzing its transcripts
One of the most straightforward ways to use ChatGPT with videos is by providing the transcript, that is, the textual representation of words spoken in the video. Many video platforms, such as YouTube, automatically generate transcripts or captions you can export.
Find a step-by-step guide on retrieving transcripts from YouTube videos here later.
Once you paste a transcript into ChatGPT, it can:
- Summarize the video content: Condense lengthy lectures, tutorials, or interviews into concise summaries.
- Extract key points: Identify main ideas, arguments, or facts.
- Answer questions: Respond to specific queries about the video’s content.
- Translate transcripts: Convert the text into other languages.
- Rewrite or simplify: Adapt complex language for different audiences.
This makes ChatGPT a reliable assistant for students, researchers, and professionals who want to quickly understand or review video material without watching the entire recording.
- Break down descriptions
If you don’t have a transcript, you can describe what happens in the video—such as scenes, visuals, or spoken dialogue—and ChatGPT can help analyze or interpret that description. For example, you could say:
“ In 5:12 minutes, you’ll find the speaker showing a graph illustrating price trends in solar panels over the past five years. Tell me what about that?”
ChatGPT can then:
- Explain the significance of the graph.
- Suggest follow-up questions.
- Provide context or background information related to the topic.
While this method depends on the accuracy and detail of your description, it enables you to get insights even without full transcripts.
But there are limitations to it, like
1. Dependence on user accuracy and detail. The quality of ChatGPT’s analysis directly depends on how accurately and thoroughly you describe the video. If descriptions are vague, incomplete, or inaccurate, ChatGPT’s insights will be limited or potentially misleading. Unlike direct video analysis, this method relies heavily on human observation and interpretation.
2. Lack of contextual continuity. Since ChatGPT only receives fragmented descriptions rather than the whole video stream, it may miss important contextual cues such as transitions, timing, or emotional tone that are critical to understanding the video’s overall message or narrative.
3. No real-time or automated processing. This approach is manual and time-consuming. You must watch the video and provide descriptions, which limits scalability and efficiency, especially for long or numerous videos.
4. Limited visual and auditory nuance. Descriptions typically focus on visible elements or spoken dialogue. Still, they may omit subtle visual cues (like body language, facial expressions) or background audio (music, ambient sounds) that contribute to the video’s meaning. ChatGPT cannot infer these nuances without explicit input.
5. Potential for subjective bias. Your descriptions can be influenced by personal interpretation or bias, which may skew ChatGPT’s analysis. Different users describing the same video might produce varying results.
6. This method is not suitable for complex or fast-paced videos. Videos with rapid scene changes, complex visuals, or dense information are challenging to describe comprehensively. Important details might be missed, reducing its effectiveness.
7. No direct audio processing. ChatGPT cannot process or interpret audio tracks directly. It cannot analyze dialogue, tone, or sound effects without a transcript or detailed description of spoken content.
- Parse video metadata
When browsing is enabled, ChatGPT can automatically retrieve metadata from publicly accessible video pages. This metadata typically includes:
- Video titles
- Descriptions
- Tags or keywords
- Upload dates
- Channel or creator information
Accessing this metadata allows ChatGPT to better understand a video’s context, topic, and scope, which in turn helps it generate more accurate and relevant responses. For example, if you provide a YouTube link, ChatGPT can extract the video’s title and description to tailor summaries or answer questions more effectively, even though it cannot watch the video itself.
This capability bridges the gap between raw video content and textual analysis by leveraging publicly available contextual information, enhancing ChatGPT’s ability to assist with video-related queries.
- Analyzing video frames as Images
With the introduction of GPT-4 Vision, ChatGPT gained the ability to analyze static images, including screenshots or key frames extracted from videos. When you upload such images, ChatGPT can:
- Describe the visual content: Identify objects, people, scenes, or activities depicted in the frame.
- Interpret embedded information: Analyze charts, graphs, diagrams, or text within the image.
- Provide contextual insights: Offer explanations or background related to the visual elements.
However, this image analysis is limited to individual frames and does not extend to continuous video streams. ChatGPT cannot interpret motion, temporal changes, or narrative flow across multiple frames, as that requires specialized video processing capabilities beyond its current design.
What ChatGPT can’t do with video content
Despite its impressive language and image processing capabilities, ChatGPT has several fundamental limitations when handling video content. Understanding these constraints is essential for setting realistic expectations and effectively using the tool.
- No direct video playback or streaming
ChatGPT is a text-based AI model that cannot play, stream, or watch videos. Unlike humans or specialized video AI, it lacks the sensory inputs and temporal processing mechanisms to interpret moving images and audio in real time. This means ChatGPT cannot experience or analyze video as a continuous, dynamic medium.
- No native audio or visual processing
While ChatGPT with GPT-4 Vision can analyze static images, it cannot process raw audio or visual data streams. It does not independently interpret colors, motion, facial expressions, or audio waveforms. Video understanding requires specialized computer vision and audio processing models, which are separate from ChatGPT’s language-focused architecture.
- Cannot interpret live or embedded videos
ChatGPT cannot access or analyze videos embedded within websites or live streams. Its interaction is limited to static text and images provided by users or retrieved via browsing capabilities. It cannot interact with or interpret dynamic video content in real time.
- No autonomous visual feedback on video content
ChatGPT cannot independently provide feedback on visuals such as slides, charts, or animations within videos unless these are described in text or uploaded as individual images. It cannot infer or comment on visual elements embedded within videos without explicit user input or image uploads.
- No access to paywalled, private, or restricted videos
ChatGPT respects web access controls, including paywalls, login requirements, and robots.txt directives. It cannot bypass these restrictions to access private or subscription-based video content. This ensures compliance with copyright laws and user privacy but limits the scope of accessible video data.
How to retrieve YouTube video transcripts and use them with ChatGPT (Desktop & Mobile)
For Desktop users
Step 1: Open the YouTube video
Go to YouTube in your web browser and open the video for which you want a transcript. Ensure the video has captions available, as most professional videos, tutorials, and interviews do.
Step 2: Access the transcript
Look below the video player for the three-dot menu icon (usually near the Share and Save buttons). Click it and select “Show transcript” from the dropdown menu. A transcript panel will appear on the right side of the video.
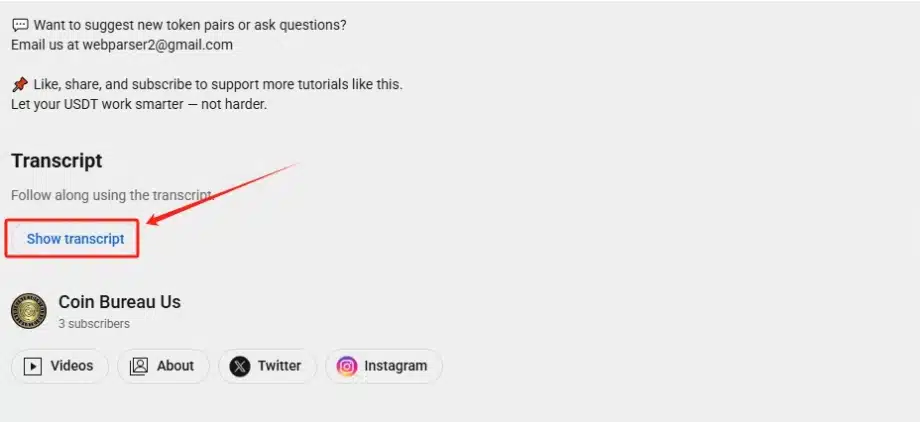
Step 3: Review the transcript
The transcript will display the video’s spoken content alongside timestamps. You can scroll through it or click any timestamp to jump to that part of the video. This helps you quickly find essential sections.
Step 4: Copy the transcript text
Click and drag your mouse to highlight the entire transcript or the parts you want. Then right-click and select Copy, or press Ctrl+C (Windows) or Command+C (Mac) to copy the text.
Step 5: Paste the transcript into ChatGPT
Open ChatGPT in a new tab or window. Click into the text input box and paste the transcript using Ctrl+V or Command+V. Now you can ask ChatGPT to summarize, analyze, or answer questions about the video content.
For Mobile users (Android & iOS)
Step 1: Open the YouTube app
Launch the YouTube app on your phone and find the video you want to work with.
Step 2: Expand the video description
Tap the “More” button or the downward arrow just below the video title to expand the description and additional options.
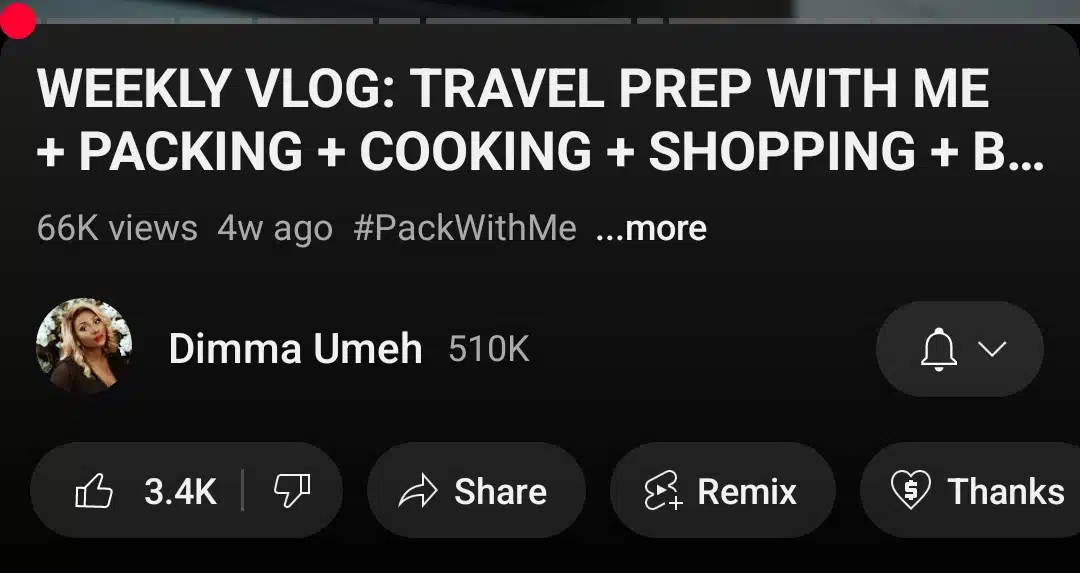
Step 3: Find and open the transcript
Scroll through the expanded description until you see the “Show transcript” option. Tap it to open the transcript panel with timestamps.
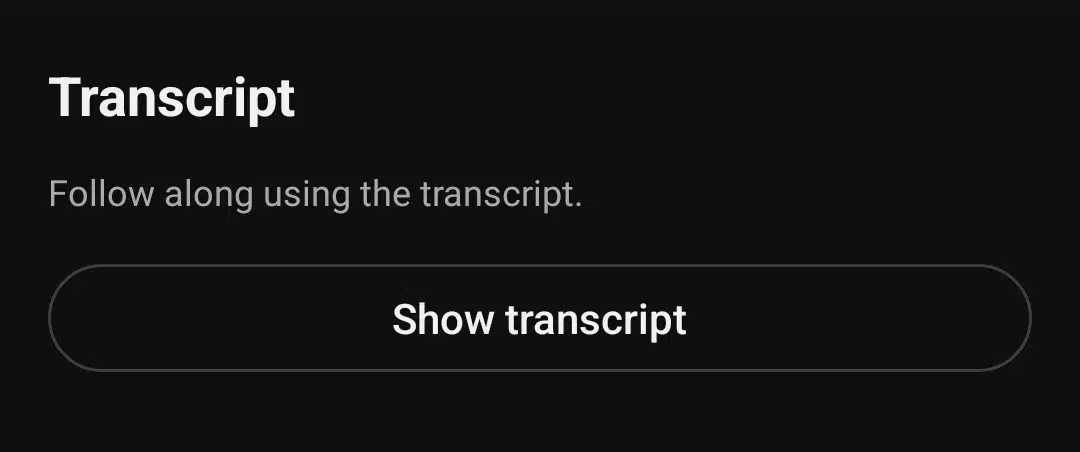
Note: If you don’t see this option, the video might not have captions enabled or transcripts available.
Step 4: Copy the transcript text
Press and hold on the transcript text until selection handles appear. Drag these handles to highlight your desired text, then tap Copy from the pop-up menu.
Step 5: Paste the transcript into ChatGPT or Notes
Switch to the ChatGPT app or your preferred note-taking app. Tap the text input area and select Paste. Now you can interact with ChatGPT using the transcript.
Bonus tips
YouTube transcripts include timestamps by default. If you prefer a clean text version, you can remove timestamps manually or paste the transcript into a text editor and delete them quickly using find-and-replace features.
Some videos don’t have transcripts due to disabled captions or privacy restrictions. In such cases, you can use third-party online tools like Rev.com, Tactiq, or Notta to extract transcripts by analyzing the video’s audio. These tools are often free and only require the video URL.
When will ChatGPT be able to watch and analyze videos?
As of mid-2025, ChatGPT still can’t watch or analyze videos independently. But the technology is moving forward quickly. Right now, in ChatGPT’s mobile apps, you can share videos, your screen, or images during conversations. This lets you interact with the AI while showing video content, but it doesn’t mean ChatGPT is actually “watching” the videos by itself.
The latest version, GPT-4o, is better at understanding images and using tools like web search, but it still can’t process full video streams or audio directly. So, while it can help with pictures or documents, it doesn’t truly “see” or “hear” videos like humans do.
Looking ahead, OpenAI’s CEO Sam Altman has said that GPT-5, expected later this year, will be able to handle videos, images, audio, and text all together. Meaning ChatGPT could soon watch videos and respond to them without needing transcripts or screenshots. It’s a big step that will change how we use AI with multimedia.
The exact release date and how well these new features will work aren’t clear yet, and they’ll probably be introduced gradually. Watching and understanding videos is tricky because it requires combining different skills, like recognizing images, understanding sounds, and following what happens over time.
There are also important privacy and copyright issues to consider, so OpenAI ensures these are handled carefully before rolling out video-watching features widely.
People really want this kind of video understanding, and it’s one of the top requests for future ChatGPT updates. As videos become a bigger part of our daily lives, having AI that can help make sense of them will be incredibly useful.
For now, ChatGPT can help with things like reading transcripts, analyzing images, and fetching video details. But soon, with GPT-5 and beyond, it should be able to watch and understand videos much more like a person.
Wrapping up,
While today’s ChatGPT cannot watch or analyze videos directly, it offers easy ways to analyze video content through transcripts, metadata, and images. These features enable users to extract valuable insights without viewing entire videos.
The upcoming GPT-5 promises accurate multimodal understanding, integrating video, audio, images, and text into a seamless experience. As OpenAI continues to add models, sooner rather than later, ChatGPT will be able to watch and understand videos like a human being, opening exciting possibilities for education, research, and creative work.
However, technical challenges and ethical considerations mean this capability will roll out gradually. For now, combining ChatGPT with existing transcription tools and metadata analysis remains the best approach to leverage video content efficiently.
Frequently asked questions about ChatGPT and video content
1. Can ChatGPT watch videos directly?
- No. ChatGPT cannot watch, stream, or listen to videos. It is a text-based AI model designed to process and generate human language. While it can analyze static images and text, it cannot process moving images or audio streams on its own.
2. How can I use ChatGPT with videos?
- You can effectively use ChatGPT with videos by providing it with text-based inputs related to the video, such as:
- Transcripts: Copy and paste the full or partial transcript of the video. ChatGPT can summarize, analyze, translate, or answer questions based on this text.
- Detailed Descriptions: Describe the video’s scenes, visuals, or spoken content. ChatGPT can interpret and provide insights based on your descriptions.
- Screenshots or Video Frames: Upload static images extracted from the video for analysis using GPT-4 Vision capabilities.
This allows you to leverage ChatGPT’s strengths in language understanding to gain insights from video content without direct video playback.
3. Does ChatGPT fetch video metadata?
- Yes, with browsing enabled, ChatGPT can retrieve metadata like titles and descriptions from public video pages.
4. Can ChatGPT analyze video frames?
- Yes, it can analyze individual images from videos, but it cannot process continuous video streams.
5. Are there interactive video features in ChatGPT?
- Recent mobile app updates allow video and screen sharing during conversations, but do not enable autonomous video watching.
6. Can ChatGPT access paywalled or private videos?
- No. It respects website restrictions and cannot bypass paywalls or login requirements.
7. When will ChatGPT be able to watch videos?
- Future models like GPT-5 are expected to have video understanding features, but are not yet available.
8. Can ChatGPT provide feedback on visuals within videos?
- Only if you describe the visuals or upload them as images it can’t interpret embedded visuals directly.
9. How accurate is ChatGPT’s video analysis?
- The accuracy of ChatGPT’s analysis depends heavily on the quality and completeness of the text or image input provided. ChatGPT can offer reliable summaries and insights when working with transcripts or detailed descriptions. However, since it does not process videos directly, any inaccuracies or omissions in the source material can affect the output. Users should always verify critical information with original sources.
10. How can I get transcripts for videos?
Many video platforms, including YouTube, provide transcript or caption features that you can access and copy. On YouTube, for example, you can click the “…” menu below the video and select “Show transcript” to view and copy the text. There are also third-party transcription services and tools that convert video audio into text, which can then be fed into ChatGPT for analysis or summarization.










