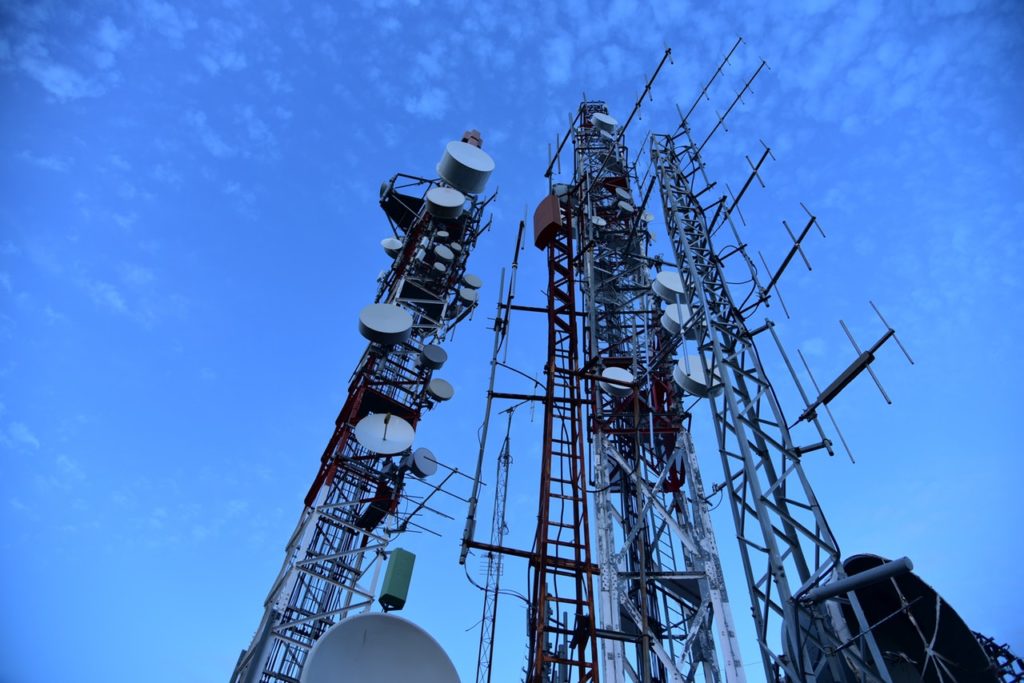
Just a few days into the lockdown on major cities in Nigeria, a lot of persons have gradually settled in on life without the usual daily commute in a bustling city like Lagos, Nigeria. Consequently, the Internet has become a lot more important as several services shifted online.
So far, there’s been no slashing of data prices by telcos. On the contrary, network services have largely stayed the same or become poorer for others. This has brought the current state of Internet connectivity to mind.
Coincidentally, there have been some puzzling speculations linking the development of 5G technology and the spread of the coronavirus pandemic around the world.
We take a look at what 5G technology is all about, its presence in Nigeria and the scientific merits of such claims.
Q: What exactly is 5G?
5G is the fifth generation of wireless communications technologies supporting cellular data networks. It is basically an upgrade from the more common 4G and is aimed at enhancing connection not only between people but also between machines, objects and devices — think advancements in emerging technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), and so on.
How is it different from other ‘Gs’?
The “G” usually associated with cellular networks stands for generation. More than 4G and other previous generations, 5G is expected to expand the capacity for mobile networks, making it possible for more devices to use the network than ever before.
According to Verizon, 2G has a maximum speed of about 50kbps (kilobytes per second) and allows basic operations like calls, SMS and MMS. 3G networks reach up to 2mbps (megabytes per second) when stationary.
4G, which is the current standard, is 500 times faster than 3G and supports more advanced activities like HD video streaming and video conferencing with speeds of up to 100s of Mbps.
The main way 5G differs from all of the previous generations is in its peak capacity and reduced latency, which is the time between when information is sent from a device until it is used by a receiver.
Who owns 5G?
5G is not “owned” by any one person, however, like with previous generations, companies can own patents in the technology, in essence earning royalties from implementers.
According to a 2019 Wall Street Journal report, Chinese companies Huawei and ZTE Corp. have put forth vastly more proposals —and are among the biggest owners of key 5G patents.
Beyond faster connections, what exactly are the benefits of 5G?
While the move from 3G to 4G LTE was about faster connections, experts say the evolution to 5G is much more and the benefits it will bring to society in the coming decade are truly revolutionary.
In addition to accelerated Internet speed, 5G is said to fast-track the mass adoption of technologies that rely on Internet connectivity, from connecting self-driving cars and drones to virtual reality, remote surgery and Internet of things.
It is very likely that 5G will take these most talked about technology trends mainstream in the coming years.
How is 5G transmitted, will it replace fibre and 4G?

Fibre optic cables are currently the fastest means of transmitting Internet connectivity and 5G technology will make use of the existing fibre backbone in Nigeria.
Nigeria has made some strides in the development of fibre connections and most base transceiver stations (telecom masts) are connected by fibre optic cables.
According to a discussion with a telecom service engineer, with 4G already installed in telecom sites, 5G devices (small cells) will be installed within short distances of each other as determined by user needs.
Hence, it appears 5G will be integrated into the existing Internet framework such as the fibre backbone, telecom masts and 4G technology, and will serve as an upgrade to improve wireless connections.
How many countries have 5G and what’s the effect there?
Countries like the US, South Korea, the UK, Germany have since deployed 5G network in some of their cities and have begun selling its compatible devices to other countries as well.
According to some analysts, 5G will account for 20% of global connections by 2025 and companies like Huawei, Ericsson, Qualcomm, Samsung, ZTE, Intel and Nokia are spearheading the charge for its mainstream adoption worldwide.
5G deployment is still in its infancy so it’s too early to state the effects it has had on these countries so far.
Do we have 5G in Nigeria?
As of this publication, there is currently no 5G network or technology available in Nigeria. Also, according to the Nigerian communications commission, no 5G spectrum has been licensed to telcos as of today.
Last year, the NCC gave permission for MTN to test the possibilities of 5G technology in three major cities — Lagos, Abuja and Calabar. A demo that was limited to their offices in those locations, lasted for three months and has since concluded.
Suggested Read: 4 things we learnt from MTN Nigeria’s 5G demo
This was, however, just a prototype or proof of concept as it were, and there is currently no fully functioning 5G network in Nigeria or by extension, Africa. The NCC has confirmed that 5G spectrums (radio frequencies) are available to be distributed when the time is right.
The National Frequency Management Council (NFMC) Chaired by the Hon Minister of Communications and Digital Economy has the responsibility for allocating bulk spectrum for various services.
When will 5G come to Nigeria?
5G development is still in its infancy worldwide, hence, no exact time can be given to when 5G will come to Nigeria.
Though Nigeria’s National broadband plan of 2013, projected a 70% 3G/4G penetration by 2018, it could only achieve 74% 3G coverage by 2019 and 4G is only present in a handful of capital cities in the country.
Also, according to a number of studies, and some observations, Nigeria’s Internet speed is a far cry from what is obtainable in other countries of the world.
It is worth noting that Nigeria envisions a 90% 4G/5G penetration by 2025, but based on the outcome of previous years, we are more likely to see massive rollouts and expansion of 4G services throughout the nation.
Suggested Read: Nigeria wants to achieve 90% 4G/5G national broadband coverage by 2025
Can 5G be used as a weapon?
5G is a telecommunications technology, not a military technology, and since we’ve established its health effects are greatly subdued, 5G itself cannot be directly used as a weapon.
However, according to a report by the US congressional research service (CRS), the capacities of military technologies will be greatly improved with the increased speed that will be engendered by 5G technology.
The CRS states that military technologies and services such as autonomous vehicles, command and control (C2), logistics, maintenance, augmented and virtual reality, and intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) systems, will receive a big boost from 5G.
On the flip side, the report also suggests that manufacturers of 5G infrastructure, should they so choose, could use it for intelligence gathering and provide backdoor access to private government and citizen data.
However, it is worth noting that since the explosion of the Internet, privacy has been a global concern, and the introduction of 5G could make the process of committing cybercrimes a lot faster.
Does 5G cause harmful radiation and is it more dangerous than 4G and 3G?
Before the coronavirus outbreak, there were already discussions regarding 5G effects on people’s health due to its higher frequencies and the type of radiation it emits.
Unlike electromagnetic radiation which can cause cancer, 5G produces a form of radiation that is not thought to penetrate and damage human cells and although 5G frequencies are a bit higher than that of 4G and 3G, the World Health Organisation has this to say about the new technology.
“To date, and after much research performed, no adverse health effect has been causally linked with exposure to wireless technologies. Health-related conclusions are drawn from studies performed across the entire radio spectrum and provided that the overall exposure remains below international guidelines, no consequences for public health are anticipated.”
Is 5G responsible for coronavirus or its rapid spread?
No. Responding to this claim, the NCC stated that there is no correlation between 5G Technology and COVID-19. Also, the World Health Organisation (WHO) says “a large number of studies have been performed over the last two decades to assess whether mobile phones pose a potential health risk (and) to date, no adverse health effects have been established as being caused by mobile phone use.”
According to the European centre for disease control, coronaviruses are a family of viruses that circulate among animals and sometimes humans. The COVID-19 virus is a new strain that has previously been undiscovered in humans.
According to WHO, the Coronavirus disease spreads primarily through contact with an infected person when they cough or sneeze. It also spreads when a person touches a surface or object that has the virus on it, then touches their eyes, nose, or mouth.
There is currently no research linking the coronavirus and telecom technologies such as 5G.
Essentially, if you notice any COVID-19 symptom after coming in contact with any telecom device, it might be as a result of prior contact with an infected person, and not the telecom device itself.
Featured image by Macau Photo Agency on Unsplash