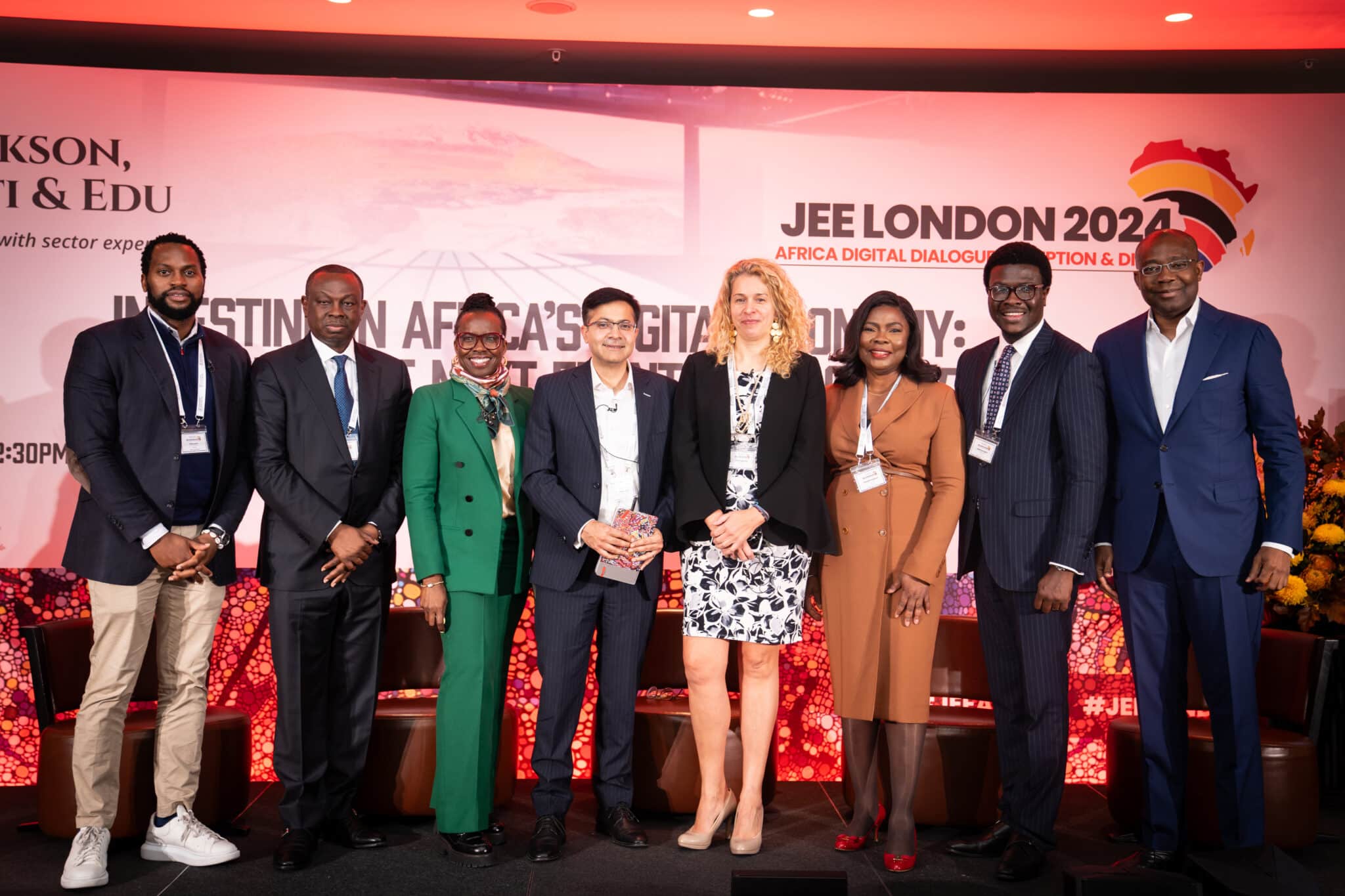
Jackson Etti & Edu (“JEE”), a leading Pan-African law firm based out of Lagos, Nigeria, hosted the Africa Digital Dialogue Reception and Dinner on 28th October, 2024 at Bulgari Hotel, London, United Kingdom. The event brought together industry leaders, investors, and policymakers to discuss the opportunities and challenges within Africa’s digital economy. The event explored the essential requirements for a robust digital economy, including digital infrastructure, e-commerce growth, regulatory frameworks, and innovative financial solutions.
The Africa Digital Dialogue
Opening remarks from JEE’s Co-Managing Partner, Fola Olusanya, emphasised the importance of strategic collaboration and investment to unlock Africa’s digital potential. She reiterated that to leverage the benefits of the digital economy, conversations on finance and investments are pertinent to achieve a viable digital economy in Africa.
The keynote speaker, Aigboje Aig-Imoukhuede, CFR, Chairman of Access Holdings Plc, highlighted the accelerating shift from traditional trade to the digital economy based on the ability of the digital ecosystem to connect people and businesses within marketplaces seamlessly. He emphasized that tech companies are highly valuable because they have mastered the art of connecting people, businesses, devices and data and not because they own physical assets. He highlighted the role of enabling digital infrastructure, e-commerce and online/ digital marketplaces and platforms in transforming the digital ecosystem. The Keynote Speaker stressed the importance of growth of digital businesses from “mice” (small ventures) to “gazelles” (fast-growing firms) and thereafter to “unicorns” (billion-dollar enterprises). Alluding to David Birch illustration in his book Job Creation in America: How Our Smallest Companies Put the Most People to Work, he explained that the most successful “gazelle” companies are the ones driving innovation and growth in the digital economy. He emphasized that the most opportunities to innovate are in the digital economy and this presents enormous investment potential.
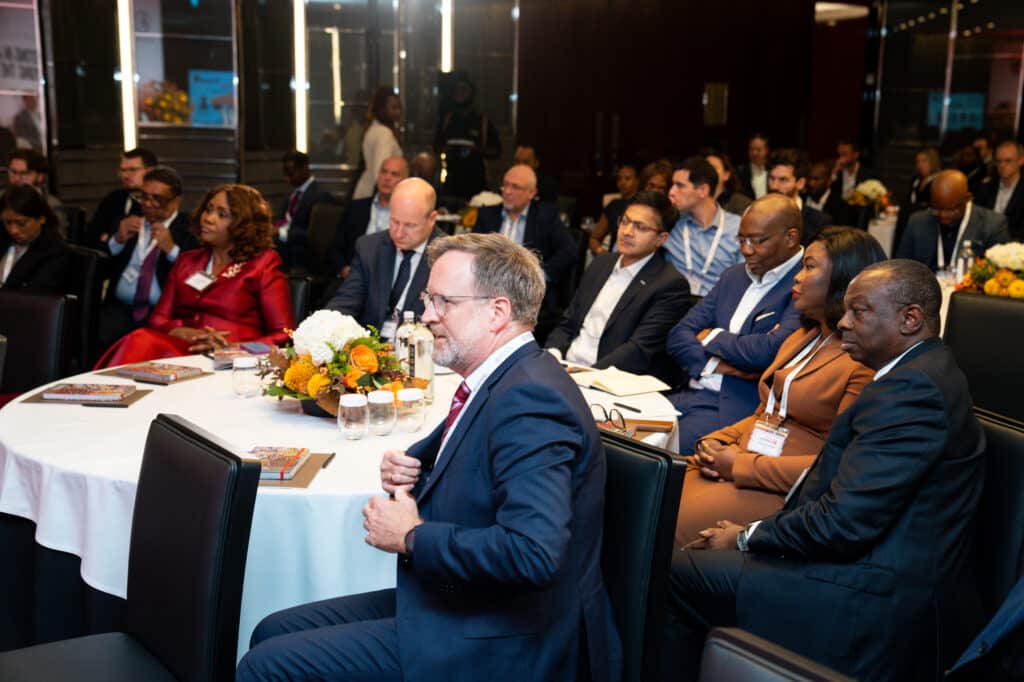

Key Issues Discussed
Salient issues were discussed and distilled from the keynote address, first panel session titled Developing Sustainable Digital Economy for Africa: Opportunities & Challenges, second panel session titled Financing the Future of Africa’s Digital Economy and the Closing Insights on Sustainable Financing for Africa’s Digital Infrastructure. The issues are outlined below: –
- Connectivity as the Source of Value: Africa must prioritize connectivity i.e. the ability to connect people, businesses, devices and data to create the “network effects” which is the aggregated network of people, businesses and data transacting value on a digital platform. This will provide the opportunity to attract value and investment.
- Unlocking Value in Underserved Markets: Investment in underserved markets such as providing free and subsidized digital services will be critical to unlocking value in underserved markets and actualizing new frontiers of investment opportunities.
- Role of Partnerships and Local Collaboration: Collaboration with local stakeholders in a bottom-up build-up process is essential for sustainable growth in the digital economy. Working closely with local providers to build inclusive technology solutions aligned with Africa’s unique market needs will result in value solutions and outcomes.
- Community Digital Skills Acquisition: All stakeholders like government, businesses, NGOs, and community members need to collaborate to leverage opportunities in the digital economy to promote digital literacy. Digital skills and literacy programmes should involve local community members, address local community needs, be adaptable to local cultures and languages and empower local ambassadors to drive adoption and sustainability. The Digital Ambassador Programme in Ghana is a successful example in this regard.
- Data Protection: The following were recommended in relation to data protection legislation and regulations:
- data protection laws should build trust and accountability, allowing individuals to understand and control the use of their data;
- efforts of the African Continental Free Trade Agreement’s digital trade protocol should ensure regulatory certainty and unity across the continent; and
- African data protection regulatory agencies should prioritize building regulatory capacity, and clearly understand and shape digital economy policies.
- Fit-for-Purpose Data Protection Regulations: African data protection laws should take into consideration necessary nuances to fit the local context and not necessarily be modelled after data protection legislations of other developed countries.
- Inclusivity in AI Adoption: AI should be adopted to drive efficiencies and productivity across key sectors of the African economy. However, it is essential to ensure inclusivity in AI adoption as well as build public trust and understanding around AI adoption, particularly with respect to concerns around job losses.
- Diversified Funding: In order to close the funding gap, Africa will require diversified funding including increased domestic funding and innovative financing options, such as venture debt, equity financing, and mezzanine investments, to support Africa’s start-ups. The importance of local currency financing to mitigate currency risks and strengthen local economies was also emphasized.
- Policy Support: A supportive regulatory environment is vital for attracting investment. Clear, investment-friendly policies, including tax incentives, create favourable conditions for the growth of tech start-ups. Governments should implement policies that encourage domestic investment and foster an environment conducive to innovation. Affordable business services such as legal and accounting are also essential to support the development of Africa’s startups.
- Human Capital Development: African governments need to develop incentives for attracting and retaining talents and invest in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics) education, digital literacy, and technical training to address the continent’s skills gap.
- Gender Disparity in Technology Adoption: Inclusive digital skills programmes, especially for women, are crucial to ensuring that all segments of society benefit from Africa’s digital transformation. There is the need to intentionally develop educational and entrepreneurial initiative that promotion representation and participation of women and the girl child in the digital ecosystem.
- Achieving Scale for African Startups: Business models should not be copied from other regions but should rather be focused on understanding the digital needs or services required by African consumers. African startups should achieve product-market fit early in view of the structural challenges in Africa, startups need to get to product-market fit faster than their global competitors to be able to scale effectively. In addition, African startups should closely monitor and optimize unit economies from early stage, as the macro environment in Africa often become challenging.
- Investment in Digital Infrastructure: Sustainable infrastructure, such as data centres, broadband connectivity, and reliable power, are fundamental to a thriving digital economy. Public-private partnerships (PPPs) are recommended as effective mechanisms to fund large-scale infrastructure projects tailored to Africa’s unique needs. Investing in infrastructure, should also dovetail into affordable data, high-speed internet and smartphones in order to bridge the digital divide.
- Financing support: Mobilizing sustainable financing from public and private sources to invest in renewable energy infrastructure, transmission, and distribution can help overcome the challenges of weak public finances and macroeconomic stresses. Such renewable energy infrastructure can be leveraged in the digital economy.
- Technology partnerships: Collaborations between public entities and private companies can facilitate the adoption of rapidly evolving renewable energy and digital technologies, allowing Africa to leapfrog more developed markets.
- Capacity building: Joint efforts to develop local skills and expertise in renewable energy project development, operations, and maintenance can ensure the long-term sustainability of these solutions in the digital ecosystem.
Conclusion
The reoccurring thoughts of Africa Digital Dialogue, hosted by Jackson Etti & Edu, that will be necessary for creating a dynamic digital ecosystem in Africa are (a) prioritizing connectivity and creating value through the creation of digital platforms that connect people, businesses, devices and data for valuable interaction and engagements; (b) unlocking value in underserved markets through partnerships with amongst governments, businesses, NGOs and community to elevate digital skills and literacy as well as empower local ambassadors to drive adoption and sustainability; (c) the need for African government to develop incentives for attracting and retaining talents including investment in education, digital literacy and technical training; (d) embracing gender diversity in technology adoption and developing initiatives to promotion participation of the female gender in technology; (e) providing incentives for investment in digital infrastructure including data centres, broadband connectivity and renewable energy.
Call to Action
The Dialogue concluded with a unified call to action:
- Governments are urged to implement clear, investment-friendly policies and prioritise the development of digital infrastructure, including affordable internet access and energy solutions while ensuring regulatory certainty and safeguarding data protection. Government should also create incentives for investment in digital infrastructure prioritizing infrastructure that facilitate universal access to the internet, efficient payments systems and access to affordable data.
- Private sector entities should support in the creation of innovative financing mechanisms, forge strategic partnerships with local stakeholders, and champion scalable, context-specific solutions and products that are able to address to Africa’s unique market dynamics.
- Development partners and civil society organisations are encouraged to support digital literacy initiatives, particularly for women and underserved populations, fostering inclusivity within the digital economy and unlocking value in underserved regions and markets. Through these efforts a more digitally empowered society can emerge creating a platform for a dynamic digital ecosystem.
- Entrepreneurs and start-ups are advised to focus on early product-market fit, streamline operational efficiency, and scale solutions that address Africa’s structural and economic realities. In adopting this strategy, entrepreneurs are better positioned to drive innovation, create value and scale their businesses.
The Africa Digital Dialogue reaffirmed that the time for action is now. A concerted effort from all stakeholders will unlock the immense potential of Africa’s digital economy, driving the continent towards inclusive, sustainable, and globally competitive African market.
Jackson, Etti & Edu