In the last fifty years, we have seen the world move from the traditional economies of the past, reliant on trade and extractive industries; to knowledge-based economies where knowledge and skills have become central to economic output – increasingly led by service sector businesses. Sustainable economic growth is directly traceable to substantial investment in service infrastructure and with Nigeria’s recent emergence from a recession, the time to ensure that growth is now.
Today, services make up over 50% of Nigeria’s GDP, and service industries are expected to continue to drive future growth. Digital financial services alone have the potential to add 12% to Nigeria’s GDP by 2025. Over the past decade, Nigeria has become the largest telecommunications market in Africa despite infrastructural deficits. The existing gaps in the mobile and data networks market, present the opportunity for significant growth that is expected to spill over into development in the country’s other sectors.
Telecommunications did not always connote the same imagery it does today. Before the internet, landline telephones and telegraphs allowed people communicate over distances. Today, new technologies allow us to communicate with several people at once, and over video: essentially connecting individuals and businesses to a series of socio-economic value chains; – in real time. As such, modern economies are becoming increasingly driven by networks; and ensuring access to those networks is fundamental to growth. In facilitating the flow of information, the telecommunications industry performs an indispensable market function of. By removing geographical barriers to trade. The industry therefore acts as a core enabler for wider economic growth and incentivizes investment. Essential to the new knowledge economy; is this flow of information across borders. , in this way; to this end, telecommunications may well provide the infrastructure of the future: that is, by facilitating the flow of information and skills that are central to the knowledge economy.
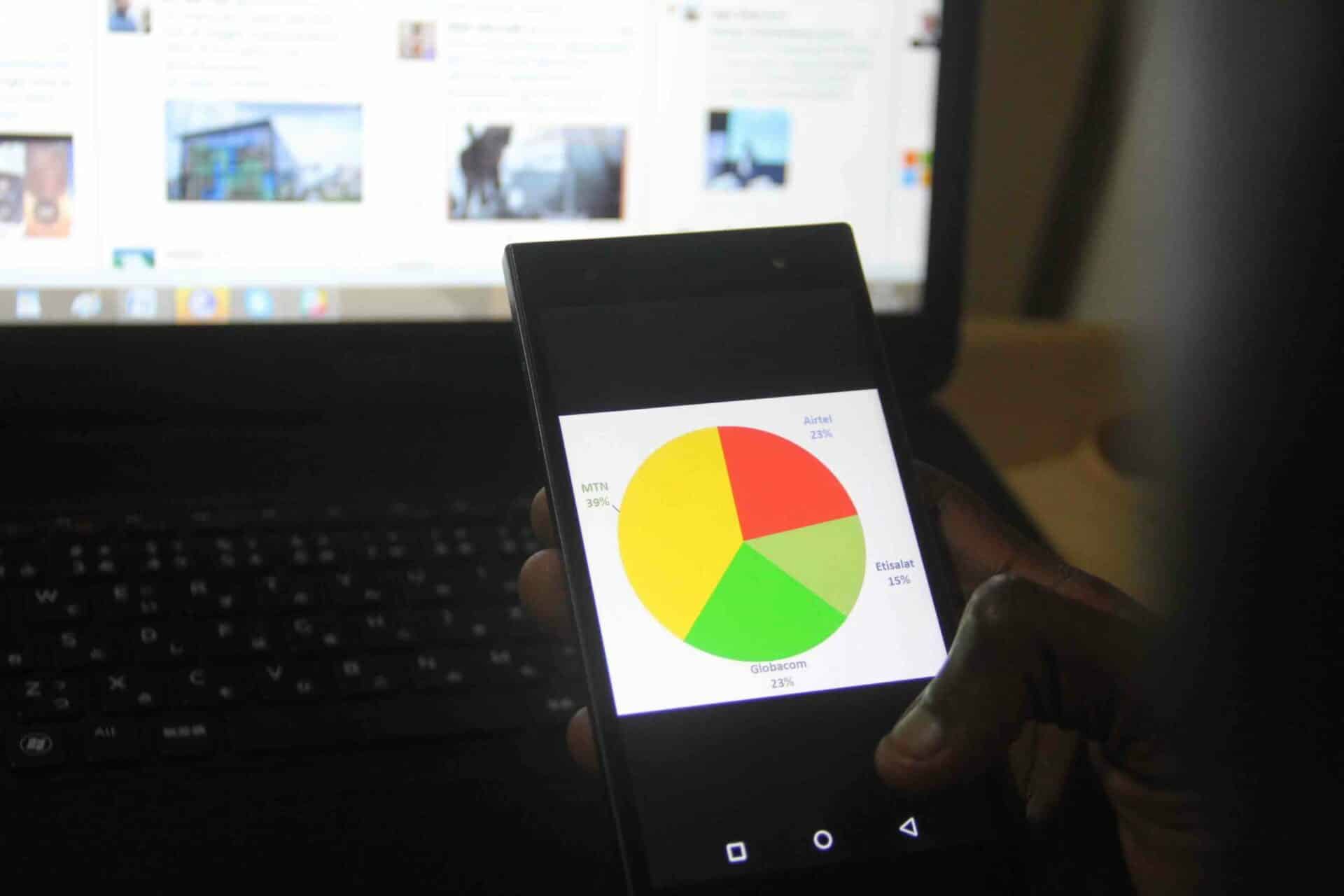
From just 500,000 customers 17 years ago, MTN Nigeria has evolved to provide voice and data network coverage, and critical digital financial service provide digital financial services and mobile and data network coverage to over 50 million Nigerians – expending over N800 billion in network infrastructure. MTN Nigeria is breaking barriers to by democratising voice and data connectivity, by and providing an increasing better quality of service to customers customers increasingly better quality of access to networks.
Each successive generation of mobile network technology improves both the voice and data experience. Currently, the company provides voice SMS and digital financial services on 2G to rural customers, ensuring that even where there are infrastructural gaps, marginal customers are still connected to the socio-economic chain in some way. 3G and 4G/LTE customers form the bulk of MTN’s 53 million customers; the former offering web-browsing and access to the OTT ecosystem; and the latter; higher-speed data and video streaming services. This is set to evolve even further. With the possibility of 5G network services looming, Nigerians could soon see data speeds up to one hundred ten times faster and , over shorter distances than 4G networks.
But speed isn’t the only benefit. Apart from speed, 5G network infrastructure will be a key asset to support societal transformation, leading to the fourth industrial revolution impacting multiple sectors1. Healthcare for example, is becoming increasingly reliant on the internet to support and provide medical services. Expectedly, healthcare will benefit from remote diagnostics and telesurgery, as well as improved treatment outcomes that result from higher quality wearable technology[1].
The instant response times because of lower latency that will accompany 5G, will vastly improve quality of living; as users obtain a better experience of everything else – from digital financial services for example, to self-driving cars which will become more feasible than is currently possible on current 4G/LTE bandwidths and latencies. Massive Machine type communication of 5G would enable a proliferation of smart home devices, logistics and utility metering. This next generation of mobile network will inspire the emergence of new vertical industries and stimulate innovation; leading to smarter cities and healthier people.
Recent estimates posit that the 5G value chain itself could support as many as 22 million jobs worldwide.[2] The total contribution of 5G to real global GDP from 2020 to 2035 is expected to be around $3 trillion: equivalent to an economy the size of India.[3] 5G is not just another network. It will form the basis of an ecosystem of financial and socio-economic sensors; blurring geographic and operational borders beyond anything we have ever seen. The possibilities are endless.
Financial instruments have set the framework for modern economic exchange, but it is new technologies that have led the evolution of the flow of money, skills and information. As technology advances, telecommunications providers will continue to seek to morph from mere commodity service providers, into providers of products and services that enhance customers’ consumers’ lives and improve the profitability of enterprise business by ensuring ease and efficiency. In this regard, MTN Nigeria is leading the pack and answering the call to provide a platform of possibilities for Nigerian consumers and businesses people; in furtherance of the Nigerian dream.

Chief Transformation Officer, MTN Nigeria
BIO
Bayo Adekanmbi is the Chief Transformation Officer at MTN Nigeria responsible for accelerating business performance, innovation and advanced analytics.
Prior to this, Bayo was the Chief Marketing Officer at MTN Nigeria. In this role, he conceptualised an award-winning Customer Value/Risk Management framework that resulted in multi-billion-naira revenue growth for the company.
With over 18 years’ experience focused on Strategy, Marketing and Analytics in emerging markets, Bayo holds a post graduate degree from the University of Reading and a PHD from City University London & TIAS Business School Netherlands.
He is the convener of Data Science Nigeria, a non-profit dedicated to promoting data science in solving Nigeria’s business and social developmental problems. In addition to this, Bayo is the author of "The Future is Shared" which explores the potential of the sharing economy in emerging markets.